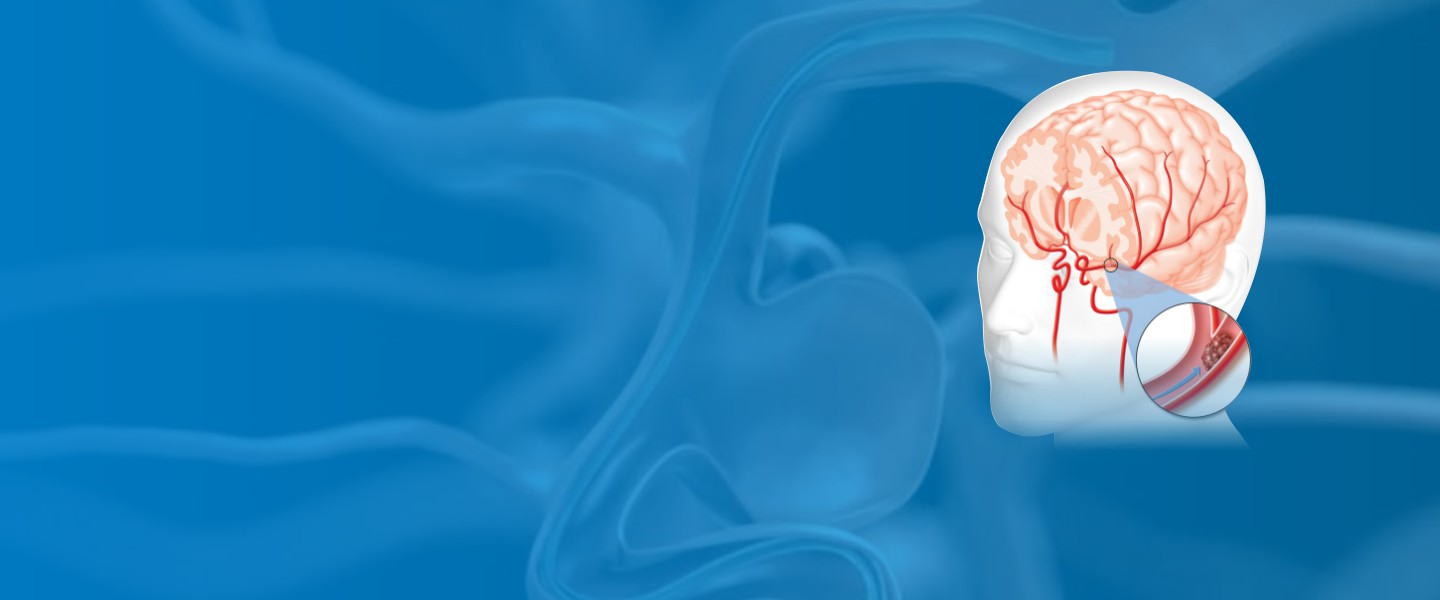
A subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a kind of stroke caused by blood clots in and around the brain. Most bleeds are due to a cerebral aneurysm, which can be either congenital or acquired through injury such as stroke. It is also possible for SAHs to develop after surgery when damage is done on one’s vessels that lead up towards their head during treatment.
A cerebral aneurysm is a weakened area in one’s brain artery (blood vessels that carry blood to your mind). The higher pressures within this section would cause it to swell outwards, eventually leading to bursting and escaping into surrounding fluids that protect all aspects inside us–including thoughts!
Symptoms of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
Most subarachnoid hemorrhages caused by brain aneurysms do not cause symptoms until they rupture. Symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm include:
- Nausea & Vomiting.
- Gradual Weakness.
- Dizziness
- Neck and Back Pain
- Severe Headache
If you face any of the symptoms stated above, you should take it very seriously and see the neurosurgeon immediately.
How to Diagnose Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
- Get a CT Scan of Your Brain –Computerized tomography of the brain is an effective and clear way to see a Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Even doing CT angiography visualizes blood vessels clearly, which is done by injecting material into a vein. CT Angiography is the better way of visualizing the hemorrhage as sometimes CT scan may miss the small subarachnoid hemorrhage which occurred a week ago.
- Lumbar puncture – A small needle is placed in the lowest part of the back to obtain cerebrospinal fluid, the fluid that bathes our brain and spinal cord. The fluid is tested for subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Brain MRI –This MRI imaging test can show if there has been “subacute” blood, or bleeding in the brain, in the recent past.
Treatment of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
- Brain Aneurysm Treatment – There are two ways to treat a brain aneurysm. One is open surgery, which is when you take the person’s skull off and put it back on again. The other way is endovascular treatment, which happens when doctors try to put a tube in the blood vessel next to the aneurysm to block it. Doctors recommend the treatment by looking at how big your brain aneurysm is and how healthy you are. If your doctor recommends open surgery despite endovascular treatment, you should go with it.
- a) Open surgical techniques:clipping or bypass open surgeries.
- b) Endovascular surgical techniques: coiling or stenting/flow diversion.
What is recovery after a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)?
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition that many factors can cause. Most patients with this type of bleeding require inpatient rehabilitation after their hospital stay and outpatient therapy for months following. It’s important to discuss what your doctor recommends. Accordingly, you can decide so nobody feels left out–even though we all want our loved ones’ mental health treated equally regardless of whether there seems any difference between each person’s situation!
What are the chances of a second subarachnoid hemorrhage?
The cumulative recurrence rate of SAH, calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method, was 2.2% at 10 years and 9.0% at 20 years after the initial treatment. So To Conclude, The recurrence risk for SAH is much higher than normal and increases with time.


Leave A Comment