What is an Angiography?
An angiography is a vital tool for assessing the health status of your blood vessels. The procedure uses X-rays to produce images of blood vessels in the body and evaluate their condition. It helps doctors identify problems, including stroke, and determine how much damage there is on various segments within them to treat accordingly.
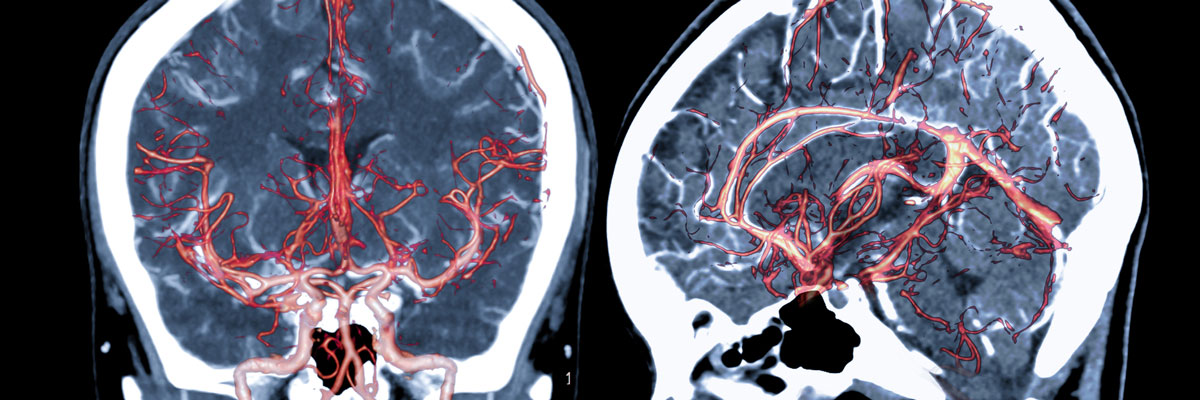
What is cerebral angiography?
Cerebral angiography is a medical imaging procedure involving inserting an artery catheter into your arm or leg, then injecting dye to visualize the blood vessels in cerebral tissue. X-ray images from this process show abnormalities within certain parts of our brain responsible for processing thoughts.
During a cerebral angiogram, highly specialized doctors such as neurosurgeons can observe all the blood vessels in one’s head using modern, sophisticated imaging equipment. To take clear pictures of the Brain, dye is injected into vessels through tiny tubes called catheters that pass right into your brain – there’s not much they can do without an x-ray!
How is a Cerebral angiogram useful?
An angiogram can also help treat some of the conditions involving the blood vessels of the neck and brain. Cerebral angiography can help to diagnose:
- Cerebral aneurysms
- Vascular malformations
- Vascular tumors
- Strokes
- Stroke-related syndromes
- Brain tumor
- Blood Clots
Cerebral angiography is useful for doctors to diagnose the issue behind the different symptoms such as:
- Different Types of Headaches.
- Loss of memory.
- Blurred or Double vision.
- Weakness or Numbness.
- Loss of Balance.
- Slurred Speech.
How is Cerebral Angiography Performed?
Before this procedure, you will have to take your clothes off. You will put on a gown that the hospital gives you. A needle with an anesthetic will be used (the needle looks like a little thing). This needle is put in your arm or leg, making you feel like nothing happens. Next, they use another needle to put the catheter in your carotid arteries (in your neck). The catheter goes through blood vessels in your brain. The radiologist (a person who looks at images) and the technologist (a person who runs machines that make pictures or x-rays) stay with you while this happens. You don’t need to worry as You will be awake during the procedure, which may take from one to two hours to complete.



Leave A Comment